What do the results mean?
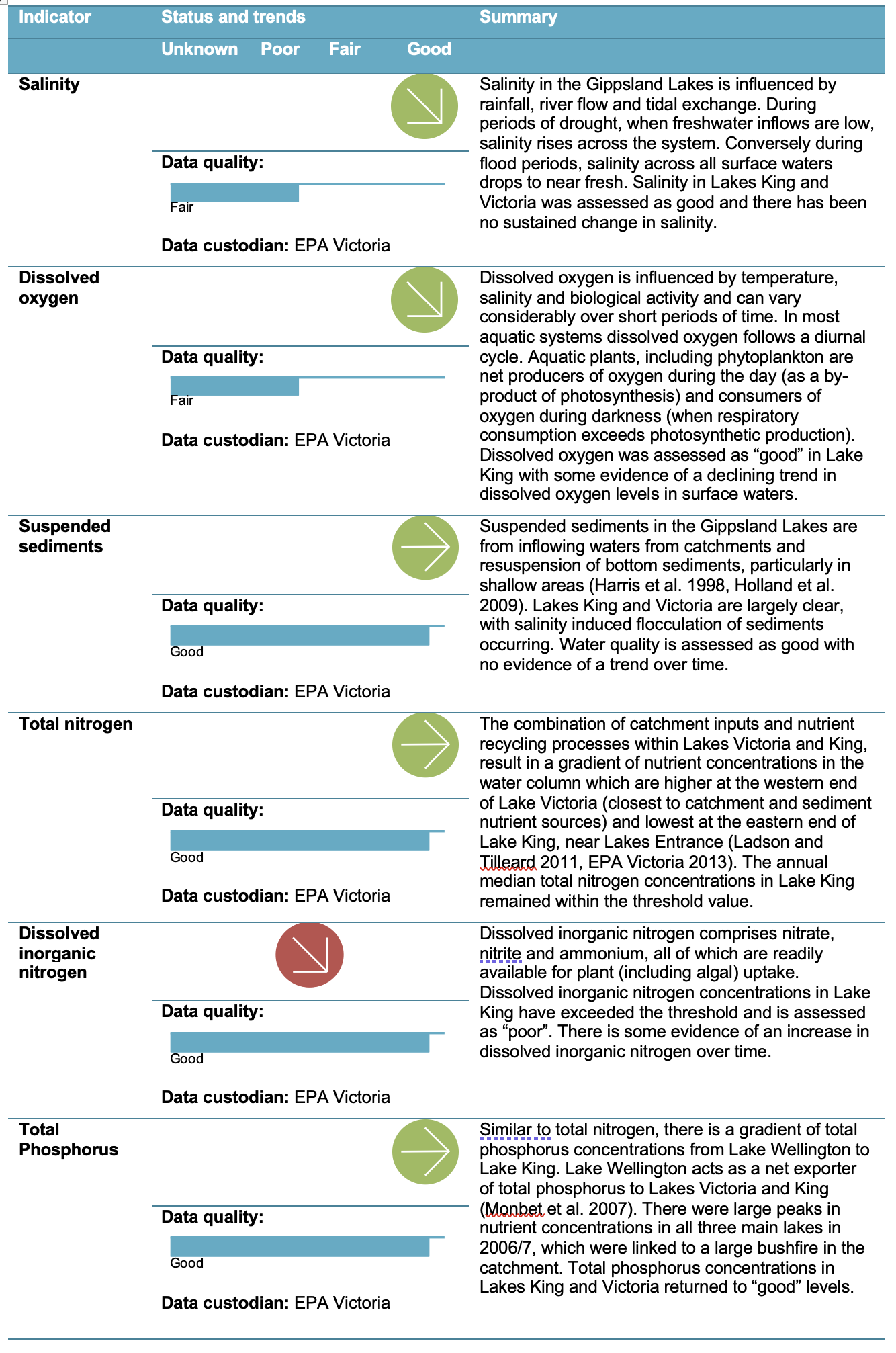
Water quality data is available for the main lakes (King, Victoria and Wellington) through EPA Victoria’s monitoring program. Results from the past five years have been compared to site specific objectives derived for the Gippsland Lakes using the national standard approach. Water quality across the lakes represents a gradient of relatively good water quality in Lake King, to poor water quality in Lakes Victoria and Wellington. Lake Wellington appears to be experiencing a sustained trend of increasing salinity.
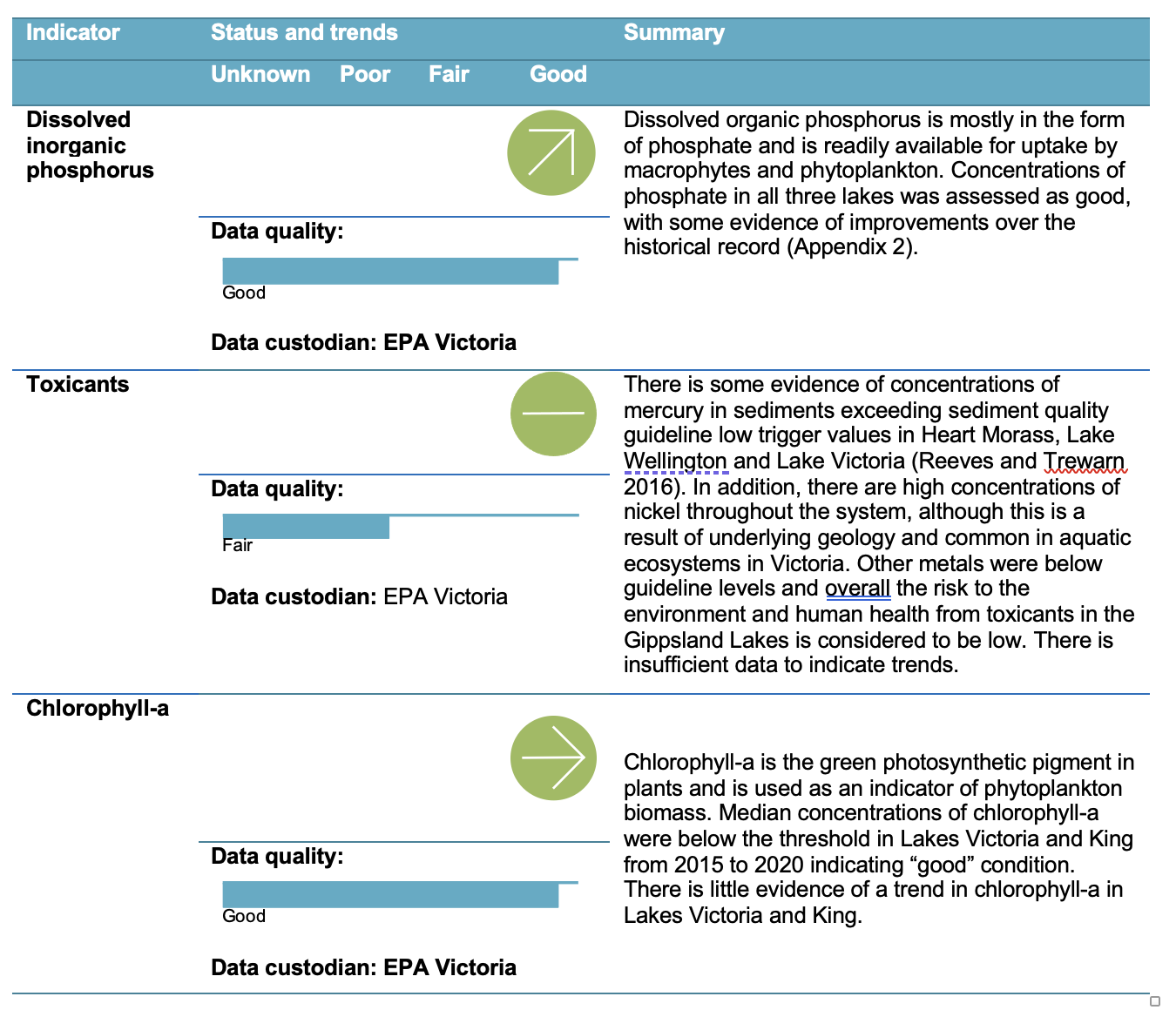
There is some evidence of concentrations of mercury in sediments exceeding the sediment quality guideline low trigger values in Heart Morass, Lake Wellington and Lake Victoria. In addition, there are high concentrations of nickel throughout the system, although this is a result of underlying geology and common in aquatic ecosystems in Victoria. All other metals were below guideline levels and overall the risk to the environment and human health from toxicants in the Gippsland Lakes is considered to be low *.
Salinity in Dowd and Heart Morass is influenced by inundation and water source. Inflows of water from the Latrobe River result in reduced salinity, but when river flows are low, more saline water can enter the wetlands from Lake Wellington. Annual median salinity was below the threshold each year (2017/18 to 2020/21) with the exception of 2018/189 in Dowd Morass. This results in a rating of “good” for Heart Morass and “fair” for Dowd Morass. There is some evidence of decreasing salinity (improved condition) in recent years, but more data are required. Two new salinity meters have been established in Macleod Morass (May 2021) and a further two will be established in Sale Common, which will allow for water quality at these two freshwater wetlands to be evaluated in the future.
*Department of Health and Human Services (2017) Mercury levels in black bream and dusky flathead from the Gippsland Lakes, Victoria. State Government of Victoria, Melbourne, Victoria.
Reeves, J.M. and Trewarn, A. (2016) Assessment of Heavy Metals and Other Contaminants of the Gippsland Lakes. Federation University Australia, Mt Helen, Victoria.